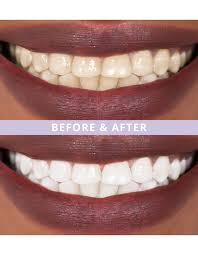
Teeth Bleaching: What You Need to Know
Teeth bleaching, a type of teeth whitening, has become popular in recent years as people strive for brighter smiles. From over-the-counter products to professional dental treatments, there are numerous options available for achieving a whiter smile. However, understanding the science behind teeth bleaching is crucial for making informed decisions about which teeth whitening method is right for you.
Understanding Tooth Discoloration: Tooth discoloration can occur for various reasons, including:
- Extrinsic Stains: These stains occur on the outer layer of the tooth (enamel) and are often caused by factors such as coffee, tea, wine, tobacco, and certain foods.
- Intrinsic Stains: These stains occur within the tooth’s structure (dentin) and can be caused by factors such as aging, trauma, genetics, or exposure to certain medications during tooth development.
The Bleaching Process: Teeth bleaching works by using bleaching agents, to break down stains and lighten the color of the teeth. The bleaching agents penetrate the enamel and dentin, where they react with the discolored molecules, breaking them down into smaller, less visible molecules.
Types of Teeth Bleaching: There are several methods of teeth bleaching, including:
- Over-the-Counter Products: These include whitening toothpaste, strips, gels, and mouth rinses that are available without a prescription. While these products can be effective for mild surface stains, they may take longer to produce noticeable results compared to professional treatments.
- Professional Dental Treatments: These treatments are performed by a dentist or dental hygienist and typically involve higher concentrations of bleaching agents for faster and more noticeable results. Common professional treatments include in-office bleaching, take-home trays, and laser bleaching.
Safety Considerations: While teeth bleaching is generally considered safe when done properly, there are some potential side effects and risks to be aware of, including:
- Tooth Sensitivity: Some individuals may experience temporary tooth sensitivity or gum irritation after bleaching treatments. This usually resolves on its own but can be managed with desensitizing toothpaste or gels.
- Gum Irritation: Overuse or misuse of bleaching products can irritate the gums and soft tissues of the mouth. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions or dentist’s recommendations carefully.
- Enamel Damage: Excessive or prolonged use of bleaching agents can potentially weaken the enamel and increase the risk of tooth damage. It’s crucial to use bleaching products in moderation and under professional supervision.
Conclusion:
Teeth bleaching can be an effective way to enhance the appearance of your smile and boost your confidence. You can make informed decisions about achieving a brighter, whiter smile while prioritizing your dental health and safety. Always consult with your dentist before starting any teeth bleaching regimen to ensure it’s appropriate for your individual needs. Currently, we have a dental bleaching offer of 20,000shs per jaw. contact us on 07 48 877 562 book an appointment today.